The skin integumentary system exercise 6 is something very essential for your body. Perhaps you never felt the importance of knowing about them better earlier. Let’s know what they are and how they function in your body.
What Is The Skin Integumentary System?
The integumentary system is the system in the body that creates a barrier between the external environment and internal systems.
This system consists of skin, hair, nails, and related glands in our body. So, you can see that together they form the body’s biggest organ. Again, this entire system has some functions.
One of the most important functions is that it protects our body parts. Such as the bones, organs, and all the internal structures of our body from the harmful effects of the outside body.
Besides, the integumentary system completes the essential immune functions. As like synthesis of Vitamin D, cell fluid maintenance, body temperature regulation, and detection of stimuli.
Where Is the Integumentary System Located?
Do you want to know? Well already told you it’s the largest organ of the body. So naturally The integumentary system will cover most of the body. Only the outer layer of the body leaves organs like our eyeballs uncovered.
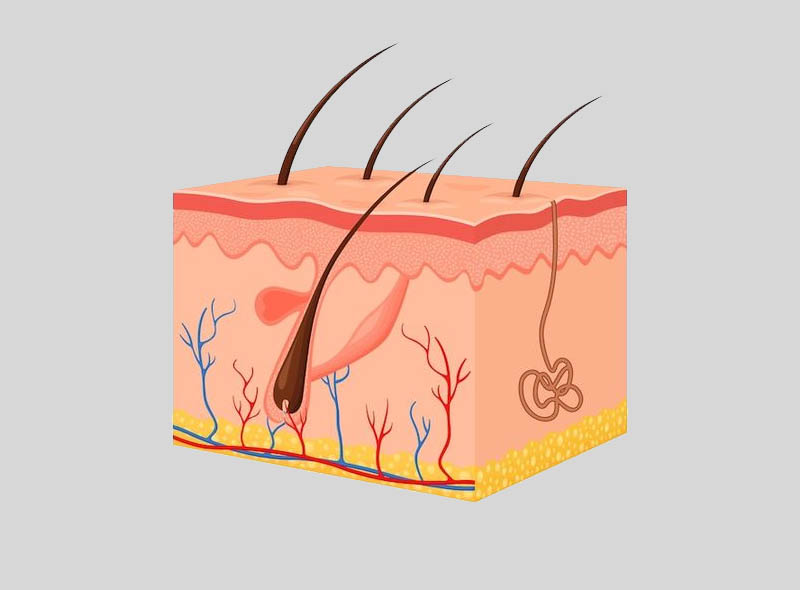
Skin: The Integumentary System is located at the outermost layers of the skin. It covers most parts of the human body, including the epidermis and dermis.
The topmost layer is the epidermis. Again, it works as the body’s first line of defense against illness and injury. The dermis is a layer under the epidermis.
It is a connective tissue that can support the epidermis. The layer has blood and lymph vessels, sweat glands, nerves, and hair follicles.
What Are The 6 Functions Of The Skin Integumentary System?
We know that the integumentary system has five components. They are- skin, hypodermis, hair, nails, and exocrine glands. These different things work together to maintain health and well-being for the rest of our body. The skin integumentary system exercise 6 has many things to do:
Protection
The two layers of epidermis and dermis together create a physical barrier. It protects all the internal body parts. Again, the skin keeps you safe from all kinds of issues we face from the environment. For example: heat, cold, and sun exposure.
Besides, the body gets protection from external ingredients. Such as viruses, bacteria, dirt, and air from the environment. In addition, there is another layer of hypodermis under your skin. It gives you some extra protection for internal organs.
Also, the hair and nails give you some additional protection. It is for other sensitive areas of the body like the fingers, toes, and face.
Nutrition
Through the process of synthesis, our body creates vitamin D. The vitamin D-making steps become active when you come to the sun. There’s no exception for vitamin D for bone health.
Immunity
The skin creates a barrier that does not allow the entry of many things. Like bacteria and viruses, infection, and preventing illness. Again, the ingredients created by the skin like lipids and antimicrobial peptides (AMPs).
They can destroy bacteria that come in contact with our skin. To activate the immune response, the immune system cells under our skin functions. It keeps sending signals to the larger immune system.
Wound Healing
Sometimes we receive many external wounds that damage our skin. If we have an injury, it triggers the clotting mechanisms. So that the bleeding stops and creates a protective layer over the wound.
Later the immune cells go to the site to prevent further infection. In The final step of healing, here comes the formation of new skin cells. Along with the formation of connections between the cells.
Temperature Regulation
Our body can endure more cold or heat than in a normal situation. It is an essential role of the skin that keeps the temperature safe.
When the body temperature rises because of external heat, things happen. Such as the blood vessels of the total surface area of our skin expand to let the heat dissipate.
Again, that secreted fluid of the sweat glands goes to be cool via evaporation. When your body becomes colder than the usual state, the skin activates the hair follicles to rise.
Thus we get goosebumps. The hairs that are raised catch the warm air near the skin and don’t let the heat leave the body.
Sensory Input
There are nerve cells in our body threaded with the skin. It helps us detect heat, cold, pain, pressure, and vibration. This sensation connects with the touch and helps you understand many things. For example- the surrounding environment and also responds properly to stimuli.
What Is The Integumentary System Skin In Answers?
What Is The Name Of The Organs Of The Integumentary System? The names of the organs of the integumentary system are the skin, hair, and nails.
What Are The Functions Of The Skin?
Here are the functions of the skin:
- Prevent water loss from your body
- Create a barrier from the entry of microorganisms, synthesize vitamin D, block UV light, and regulate the body temperature.
What Is The Composition Of Hair?
Hair is made from mainly the keratin-filled dead keratinocytes.
What Are The Three Physiological Roles Played By Hair?
They reduce heat loss from our bodies. Again, keep harmful elements out of the eyes. Finally filters particles out of inhaled air in our noses.
What Do Nails Consist Of?
Nails consist mainly of keratin-filled, dead keratinocytes. Same as the hair.
What Are The Two Functions Of Nails?
They enhance the sense of touch at our fingertips. Besides, they protect the ends of the fingers and toes.
Why Is Skin Important?
The functions of the skin are many. Some are:
- They work as a barrier and protect against water loss. Also, various physical and chemical injuries and bugs
- Our skin lets us feel the touch and provides us with interaction with physical surroundings. It allows us to do all kinds of gross motor activities. Again, it lets us feel all types of physical activities.
- Regulate the body temperature by constricting and dilating the blood vessels near the skin’s surface. It controls the heat transfer out of the body. Again, the temperature is regulated by the evaporative cooling system. The reason is sweat production and the insulation effect of raised hairs on your skin’s surface. At the same time, the loss of heat is also affected by the insulating layer of subcutaneous fat.
- Help us fight off bugs, toxins, allergens, and carcinogens through the parts of the immune system that exist in the skin
- Protects us from the radiation of the UV by producing the ingredients named melanin
- Our physical beauty and attraction depend on the quality of our skin. It contributes to the perception of health, youth, wellness, and beauty.
- Our skin produces the necessary Vitamin D. It fights diseases like heart disease, cancer, neurological diseases, and obesity.
How Many Layers Of Skin?
Three layers of tissue create the skin:
- Epidermis, the top layer.
- Dermis, the middle layer.
- Hypodermis, the bottom or fatty layer.
What Is Human Skin An Example Of?
Human skin is an example of tissue organization. As you can see, many cells form a tissue, and a lot of tissue forms the skin.
Conclusion
The skin integumentary system exercise 6 is essential to the body. Perhaps we don’t think of them or know about them a lot. But they have a lot of effective sides. It protects our body from various external things.